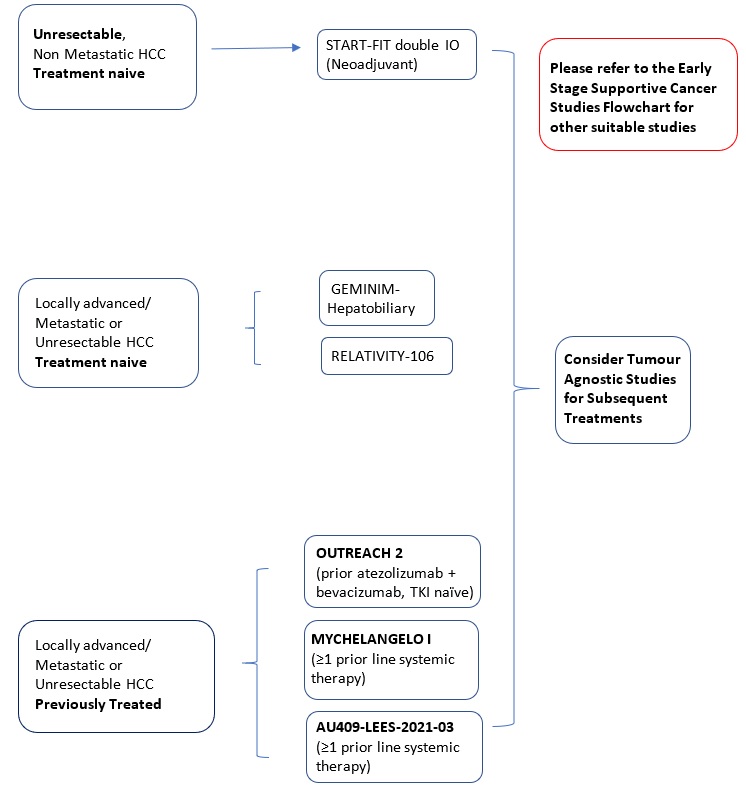

- 5.1. Clinical Trial
- 5.1.1. Liver Cancer
- 5.1.2. Cholangiocarcinoma
- 5.2. Basic Research
|
5.0 Hepatobiliary |
|
|||||||||
|
5.1 Clinical Trial |
|
|||||||||
|
5.1.1.1 Liver Cancer |
|
|||||||||
|
Non-metastatic, Unresectable |
|
|||||||||
|
Specific Selection Criteria: PD-L1, CTLA-4 |
|
|||||||||
|
First-line treatment: Phase 2 |
TACE + SBRT + Immunotherapy (Anti-PD-L1/ Anti-CTLA-4 antibody) |
|
||||||||
|
Study Title |
Main Inclusion/Exclusion |
Investigational Product |
Principal Investigator |
Department |
|
Contact number |
|
|||
|
Sequential TransArterial chemoembolization and stereotactic radiotherapy Followed by durvalumab (MEDI4736) and tremelimumab for downstaging hepatocellular carcinoma for hepatectomy (START-FIT double IO). |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
Key Exclusion Criteria:
|
Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) + Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) + Durvalumab (Anti-PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibody) + Tremelimumab (Anti-CTLA-4 Monoclonal Antibody) |
Prof. Albert Chi-Yan Chan |
Department of Surgery |
isabelw@hku.hk |
Isabel Chan 2255 5362 |
|
|||
|
5.1.1.2 Liver Cancer |
||||||||||
|
Locally Advanced or Metastatic, Unresectable |
||||||||||
|
First-line treatment: Phase 2 |
Targeted therapy (Anti-VEGF Antibody / VEGFR Inhibitor) |
|||||||||
|
GEMINI-Hepatobiliary (Protocol ID: D7987C00001): A Phase II, Open-Label, Multi-Drug, Multi-Centre, Master Protocol to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Novel Immunomodulators as Monotherapy and in Combination with Anticancer Agents in Participants with Advanced Hepatobiliary Cancer. |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
Key Exclusion Criteria:
|
Medi5752 (Monovalent bispecific antibody (PD-1 + CTLA-4)
Vs.
Medi5752 (Monovalent bispecific antibody (PD-1 + CTLA-4) + bevacizumab (Anti-VEGF Monoclonal Antibody)
Vs.
Medi5752 (Monovalent bispecific antibody (PD-1 + CTLA-4) + lenvatinib (VEGFR Inhibitor) |
Dr. Chiang Chi Leung |
Department of Clinical Oncology |
ychwilly@hku.hk |
Will Yeung 22555125 |
||||
|
5.1.1.3 Liver Cancer |
||||||||||
|
Advanced, Unresectable |
||||||||||
|
Specific Selection Criteria: Naïve to tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
||||||||||
|
Second-line treatment: Phase 2 |
Targeted therapy (VEGFR inhibitor) |
|||||||||
|
OUTREACH2 (Protocol ID: MNA-3521-014-RNDZ): An Open Label, Randomised Phase 2 Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of MTL-CEBPA Administered in Combination with sorafenib or sorafenib Alone in TKI naïve Participants with Previously Treated Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Virus. |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
|
MTL-CEBPA + sorafenib (TKI Inhibitor)
Vs.
Sorafenib |
Dr. Thomas Yau |
Department of Medicine (Medical Oncology) |
medicaloncology@hku.hk |
|
||||
|
5.1.1.4 Liver Cancer |
||||||
|
Advanced or Metastatic |
||||||
|
First-line treatment: Phase 1/2 |
Immunotherapy (anti-LAG-3/ anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody), Targeted therapy (Anti-VEGF Monoclonal Antibody) |
|||||
|
Study Title |
Main Inclusion/Exclusion |
Investigational Product |
Principal Investigator |
Department |
|
Contact number |
|
RELATIVITY-106 (Protocol ID: CA224-106): A Phase 1/2, Safety Confirmation, Placebo-controlled, Randomized Study of Nivolumab in Combination With Relatlimab and Bevacizumab in Treatment-naive Advanced/Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
|
Relatlimab (anti-LAG-3 monoclonal antibody) + Nivolumab (anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) + Bevacizumab (Anti-VEGF Monoclonal Antibody)
Vs.
Placebo + Nivolumab + Bevacizumab |
Dr. Thomas Yau |
Department of Medicine (Medical Oncology) |
medicaloncology@hku.hk |
2255 5582 |
|
5.1.1.5 Liver Cancer |
||||||
|
Advanced, Metastatic, Non-resectable, Recurrent |
||||||
|
Specific Selection Criteria: Tumor association with MYC oncogene |
||||||
|
Second-line or Subsequent treatment: Phase 1/2 |
mRNA therapeutic, Targeted Therapy (tyrosine kinase inhibitor), Immunotherapy (Anti-PD-1/ PD-L1 antibody) |
|||||
|
Study Title |
Main Inclusion/Exclusion |
Investigational Product |
Principal Investigator |
Department |
|
Contact number |
|
A Phase 1/2 open-label study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and preliminary antitumor activity of OTX-2002 as a single agent and in combination with standard of care in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and other solid tumor types known for association with the MYC oncogene. |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
|
OTX-2002 (mRNA therapeutic)
Vs
OTX-2002 + TKI 1
Vs.
OTX-2002 + TKI 2
Vs.
OTX-2002 + Anti-PD-1/L1 antibody |
Dr. Thomas Yau |
Department of Medicine (Medical Oncology) |
medicaloncology@hku.hk |
2255 5582 |
|
5.1.1.6 Liver Cancer |
||||||
|
Advanced or Metastatic, Unresectable |
||||||
|
Second-line or Subsequent treatment: Phase 1 |
RNA transcription modulator |
|||||
|
Study Title |
Main Inclusion/Exclusion |
Investigational Product |
Principal Investigator |
Department |
|
Contact number |
|
A Phase I, Single-arm, Open-label, Dose-escalation, Safety and Pharmacokinetic Study of AU409 Capsule in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Who Failed Standard Treatment (AU409-LEES-2021-03) |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
Key Exclusion Criteria:
|
AU 409 (RNA transcription modulator) |
Dr. Chiang Chi Leung |
Department of Clinical Oncology |
ychwilly@hku.hk |
Will Yeung 2255 5125 |
|
5.0 Hepatobiliary |
||||
|
5.2.1 Basic Research |
||||
|
Study Title |
Principal Investigator |
Department |
|
Contact number |
|
A study of the regulation of TAX1 binding protein 2 by p21-activated protein kinase 4 in liver cancer metastasis |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.2 Basic Research |
||||
|
A study of the role of salt-inducible kinase 2 in regulating chemo-resistance of liver cancer cells |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
Characterization of the role of liver cancer stem cell marker, CD133 in promoting chromosome instability in hepatocarcinogenesis |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.3 Basic Research |
||||
|
Functional characterization of the roles of NIMA-related kinase, Nek2 in liver cancer development and metastasis |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.4 Basic Research |
||||
|
Functional characterization of the roles of Polo-like kinase 4, Plk4 in hepatocarcinogenesis |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.5 Basic Research |
||||
|
The therapeutic potential of Polo-like protein kinase 4 in liver cancer |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.6 Basic Research |
||||
|
Characterization of novel HBx regulated gene in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.7 Basic Research |
||||
|
A study of the role of p21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) in chromosome instability |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences
|
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.8 Basic Research |
||||
|
Molecular mechanisms of Pumilio-Regulated Chromosomal Instability in Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences
|
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.9 Basic Research |
||||
|
Development of a P-21 activated protein kinase 4 specific inhibitory peptide as a novel hepatocellular carcinoma therapeutic agent |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.10 Basic Research |
||||
|
A study of the role of transgelin-2 in hepatocarcinogenesis |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.11 Basic Research |
||||
|
The role of centrosomal protein CEP295 in chromosome instability and liver cancer progression |
Dr Yick Pang Ching |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
ypching@hku.hk |
Dr Yick Pang Ching 3917 9434 |
|
5.2.12 Basic Research |
||||
|
Delineating and translating the mechanistic determinants to improve the clinical management of liver cancer |
Dr Clive Yik Sham Chung |
School of Biomedical Sciences
|
cyschung@hku.hk |
Dr Clive Yik Sham Chung 3917 9172 |
|
5.2.13 Basic Research |
||||
|
Understanding Cancer Stemness in Liver Cancer - From Regulation to Translational Applications |
Prof. Oi Lin Irene Ng |
Department of Pathology |
iolng@hku.hk |
2255 2664 |
|
5.2.14 Basic Research |
||||
|
A Multidisciplinary Study on CD133 Liver Cancer Stem Cells: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Relevance and Therapeutic Implications |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.15 Basic Research |
||||
|
A study of the role and therapeutic potential of targeting protein tyrosine kinase 7 (PTK7) in liver cancer |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.16 Basic Research |
||||
|
AGPAT4: a novel metabolic driver of stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.17 Basic Research |
||||
|
An Immune Perspective on Exploiting Stemness as a Cancer Cell Vulnerability for the Treatment of Liver Cancer. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences
|
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.18 Basic Research |
||||
|
Annexin A3: potential predictive factor for the efficacy of sorafenib and new therapeutic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.19 Basic Research |
||||
|
Development and applications of a driver-dependent tumor organoid biobank for translational liver cancer research. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences
|
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.20 Basic Research |
||||
|
Development and Pre-clinical Evaluation of a Humanized ANXA3 Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.21 Basic Research |
||||
|
An immune perspective on exploiting stemness as a cancer cell vulnerability for the treatment of liver cancer (CRF). |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.22 Basic Research |
||||
|
PRMT6 in the control of glucose metabolic reprogramming in CD133+ liver cancer stem cells. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.23 Basic Research |
||||
|
Establishment of a novel ANXA3 neutralizing antibody and its use, alone or in combination with sorafenib, as a potential therapeutic regimen against liver cancer. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.24 Basic Research |
||||
|
PRMT6 regulates ERK1/2 signal transduction in liver cancer through CRAF. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.25 Basic Research |
||||
|
Establishment, characterization and applications of normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma organoid cultures. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.26 Basic Research |
||||
|
PRMT6 binds to and methylates BAG5, BAG6, AMBRA1 and SQSTM1 to regulate autophagy in liver cancer. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.27 Basic Research |
||||
|
A pre-clinical study to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of FSTL1 neutralizing antibody in combination with sorafenib for the treatment of HCC. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.28 Basic Research |
||||
|
Molecular and mechanistic characterization of FUT1 mediated cancer stemness in a glucose restricted liver tumor microenvironment |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.29 Basic Research |
||||
|
A pre-clinical study to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of PTK7 neutralizing antibody in combination with other approved chemotherapy or molecular targeted drugs for the treatment of HCC |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.30 Basic Research |
||||
|
Molecular and mechanistic characterization of SERPINA12 mediated cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.31 Basic Research |
||||
|
Molecular and mechanistic characterization of FUT2 mediated cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma with PTEN loss |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.32 Basic Research |
||||
|
Molecular and mechanistic characterization of SPINK1 mediated cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.33 Basic Research |
||||
|
Functional characterization of fucosyltransferase 1 (FUT1) in promoting cancer stemness properties in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences
|
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.34 Basic Research |
||||
|
Regulatory role of microRNA-1246 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway interaction in CD133+ liver cancer stem cells-driven hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.35 Basic Research |
||||
|
Role of PRMT6 in regulating cancer and stemness properties in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.36 Basic Research |
||||
|
Role of protein arginine methyltransferase 6 (PRMT6) in metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.37 Basic Research |
||||
|
Role of the lipid metabolic regulator DGKH in driving stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.38 Basic Research |
||||
|
Significance of serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 1 (SPINK1) in liver cancer: function, regulation and therapeutic implication |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.39 Basic Research |
||||
|
Annexin A3 (ANXA3) as a novel therapeutic target for liver cancer |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.40 Basic Research |
||||
|
Prom1+ tumor-propagating cells and their dynamic cellular transition during liver cancer progression |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.41 Basic Research |
||||
|
Targeting uPAR in tumor-associated macrophages of hepatocellular carcinoma |
Dr. Rio Ryohichi Sugimura |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
rios@hku.hk |
Dr Rio Ryohichi Sugimura 3917 9269 |
|
5.2.42 Basic Research |
||||
|
The immune microenvironment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma |
Dr. Rio Ryohichi Sugimura |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
rios@hku.hk |
Dr Rio Ryohichi Sugimura 3917 9269 |
|
5.2.43 Basic Research |
||||
|
Exploiting stemness as a cancer cell vulnerability using hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as a model system |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.44 Basic Research |
||||
|
Using tumour mutational landscape to resolve the cellular origin of hepatocellular carcinoma at single cell level |
Dr. Jason Wing Hon Wong |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
jwhwong@hku.hk |
Dr. Jason Wing Hon Wong 3917 9187 |
|
5.2.45 Basic Research |
||||
|
Role of MAPK11 in liver cancer stem cells. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |
|
5.2.46 Basic Research |
||||
|
A multidisciplinary study on hepatic cancer stem cells. |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma |
School of Biomedical Sciences |
stefma@hku.hk |
Prof. Stephanie Kwai Yee Ma 3917 9238 |

Follow HKUMed